THE REASONS FOR MAKING SUSTAINABLE CHOICES DURING GASTRONOMIC TRAVELS
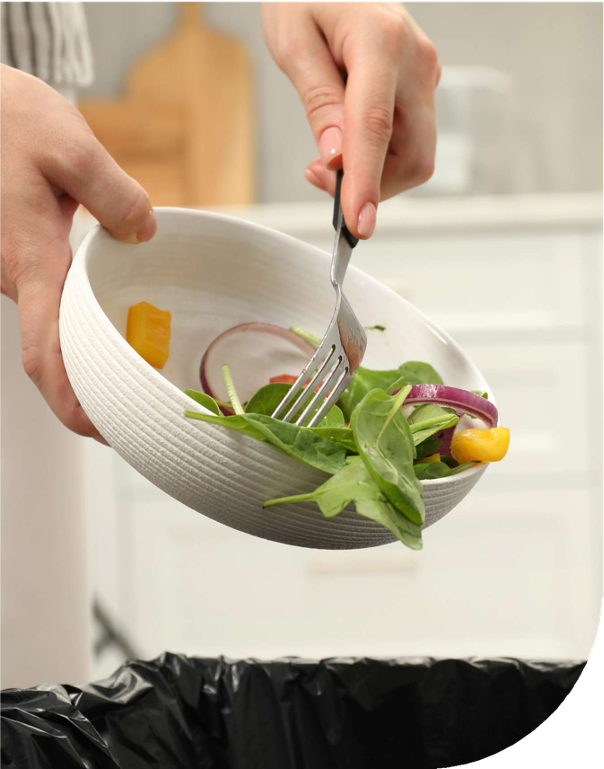

Why Not to Waste Food
Today, about one-third of the food produced globally is wasted..
WASTING FOOD MEANS:
- Negatively impacting the environment.
Approximately 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions are due to food waste. - Being irresponsible.
Around 828 million people worldwide suffer from malnutrition, and at least 11 million die from hunger or hunger-related causes, many of whom are children. - Creating unnecessary costs.
The global cost of food waste is estimated at about 1 trillion dollars a year.
*Remember: Adopting correct and conscientious behavior helps to improve the balance of food distribution and mitigate food security issues, in addition to reducing negative impacts on the environment, people, and the economy.
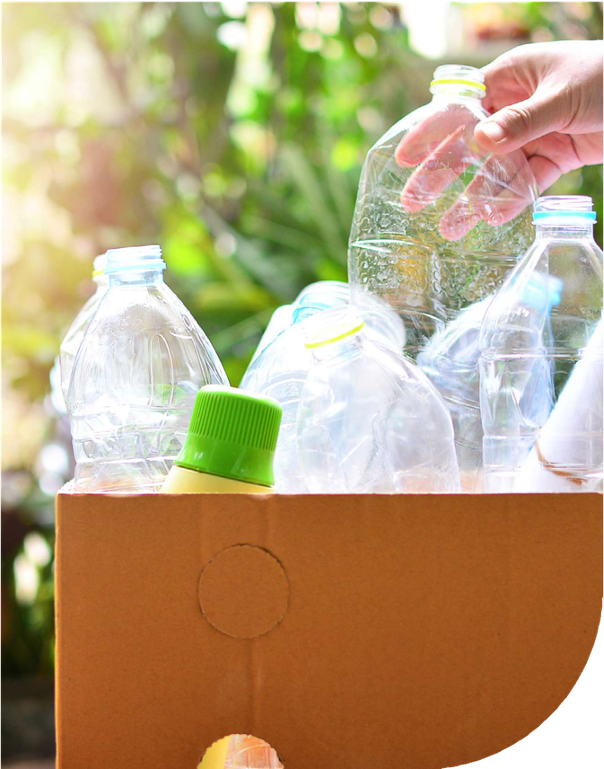

Why Recycle?
To tackle environmental challenges and support a more sustainable future for our planet,
it is necessary to shift away from the traditional paradigm based on a linear model of production and consumption in which resources are extracted, used, and then disposed of.
This means maximizing resource use and reducing waste through a circular economy based on the recycling and reuse of plastic, paper, glass, metals, and many other materials.
RECYCLING AND REUSING ALLOW US TO:
- Reduce environmental impact through resource savings and the emission of fewer pollutants.
- Generate new economic opportunities, creating jobs related to recycling, reuse, and repair.
- Foster innovation, as the circular economy requires new ways of designing products that can be reintegrated into the production system, giving them a second life.
*Remember: Each of us can play a part through tiny daily actions such as separating waste, purchasing recyclable products, and seeking reuse options. By doing so, we set a good example, encouraging others to adopt these small but effective practices.
Why Practice a Balanced Lifestyle by Eating Healthy?
Lifestyle is the main factor influencing people’s health.
It accounts for 50%, more than double that of genetics and socioeconomic status (20%), and five times more than social health care (10%).
By changing it, one can live better and longer.
THE FIRST STEP IS TO START EATING HEALTHILY AND EXERCISING. WHY?
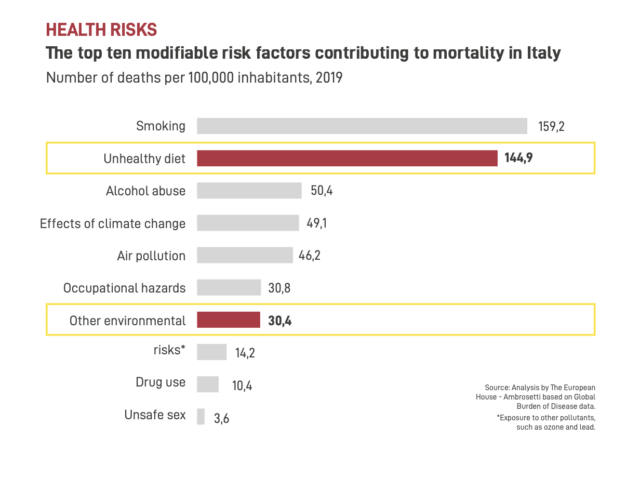
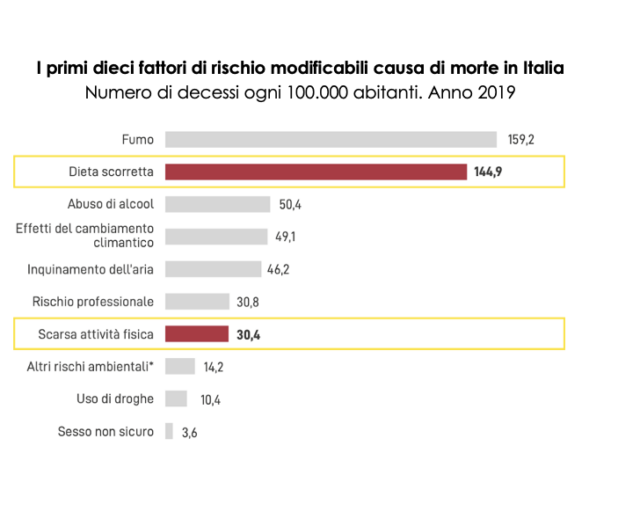
- To reduce health risks.In Italy, 23.1% of deaths are associated with poor dietary habits. An unhealthy diet increases the likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases, cancers, and diabetes.
- To stay “young”.Regular physical activity (150 minutes per week, according to WHO recommendations) helps control blood pressure and cholesterol levels, contributes to the prevention or delay of chronic diseases associated with aging, and reduces the risk of osteoporosis-related fractures and falls.
Why Follow the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean Diet is a nutritional model inspired by the traditions and eating habits of the countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea.
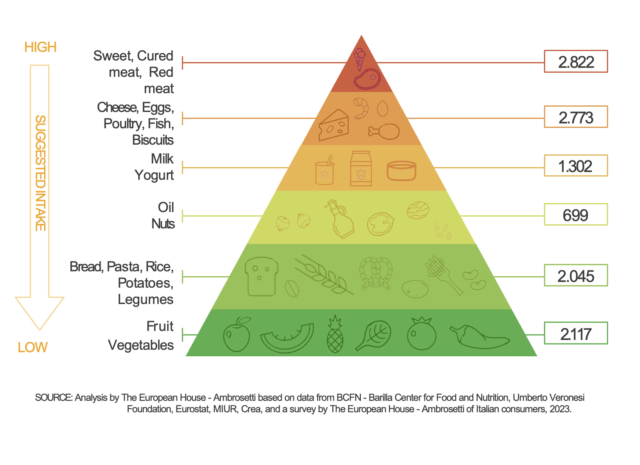
In line with the food pyramid, it emphasizes daily consumption of vegetables and fruit. Extra virgin olive oil is the preferred seasoning, along with garlic, onion, and spices. On the other hand, foods like red meats and cured meats should be consumed in moderation, with a preference for white meats or fish. Despite its importance and strong connection to Italy, only 17.3% of Italians are aware of the recommended daily fruit and vegetable intake according to the diet’s guidelines, and only 5% follow this healthy practice.
CHOOSING THE MEDITERRANEAN DIET OFFERS NUMEROUS ADVANTAGES:
- It’s Good for Your Health.The daily intake of fruits and vegetables provides essential nutrients for our bodies, such as carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and many phytochemicals (e.g., antioxidants).
- It’s Economically Sustainable. The production costs of vegetables and fruit are generally lower than those of meat, making these foods more accessible to everyone.
- It Has a Low Environmental Impact. The Mediterranean Diet offers significant environmental benefits. For example, producing 1 kg of beef emits approximately 32 kg of CO2 equivalents, while producing 1 kg of rice emits around 1 kg. Additionally, beef requires a large amount of water: about 15,500 liters for 1 kg of meat compared to just 250 liters for 1 kg of potatoes.
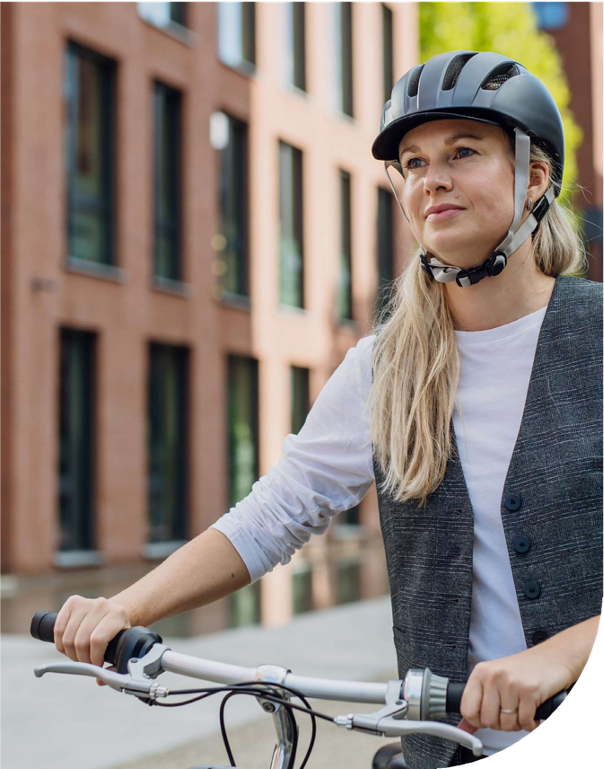

Why travel on foot or by bicycle?
Today we live in a world characterized by increasing air pollution, traffic, and sedentary lifestyles.
The importance of adopting more sober and sustainable modes of transportation is crucial and inevitable, but it requires a radical change in daily habits.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF THIS CHOICE?
- It has a positive impact on psycho-physical well-being.
It improves cardiovascular and mental health, preventing chronic problems such as obesity, heart diseases, and diabetes. Moreover, it increases endurance and muscle strength, helps reduce stress, and enhances overall well-being. - It is good for the environment.
Moving on foot and/or by bicycle helps reduce the amount of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere compared to traveling by car. This contributes to slowing down global warming and improving air quality, especially in urban areas. - It promotes the creation of more cohesive and lively communities.
Cycling and walking paths can become places for socializing and exchange, fostering a spirit of belonging and cooperation among citizens as well as a greater connection with the surrounding environment.
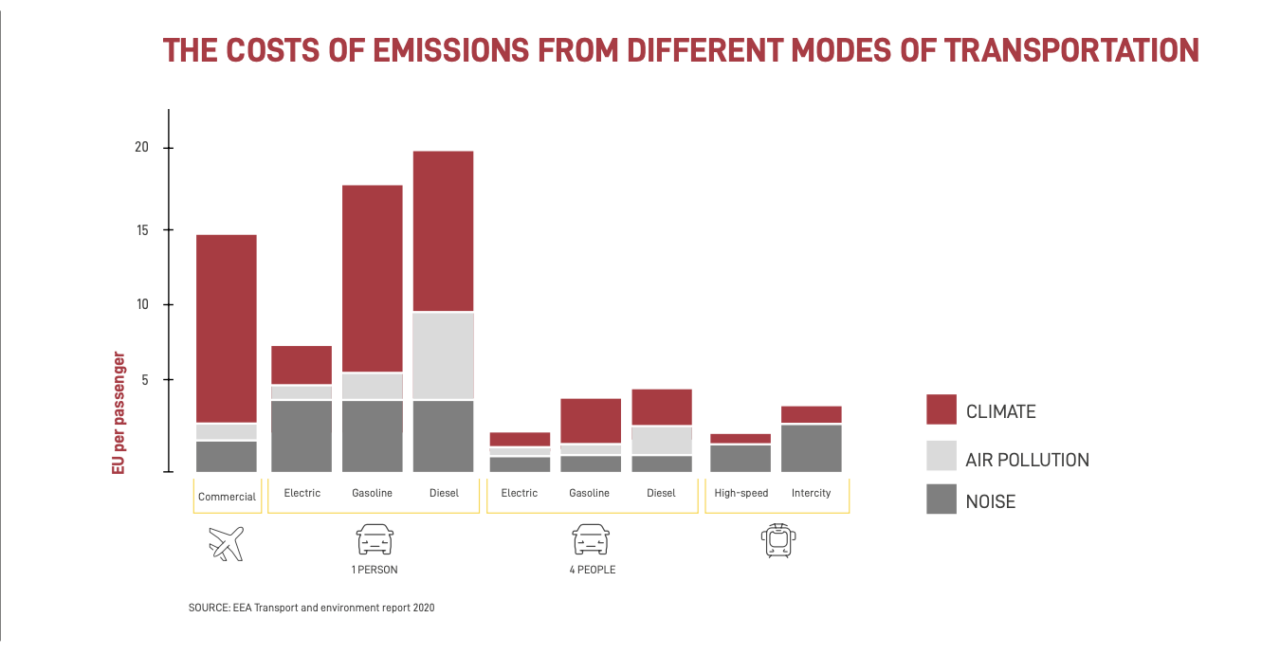
Why Choose Less Impactful Means of Transportation?
Today, we travel more and more—whether for work, education, leisure, or vacations.…
To do so, we rely on various modes of transportation (cars, airplanes, trains, etc.), which, despite their increasing efficiency, pose a serious threat to the climate, the natural environment, and public health due to greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, over the last 30 years, transportation has been the only major economic sector in the EU where emissions have increased.
While we can’t stop moving, it’s essential to do so more responsibly. For instance, when possible, choosing the train over planes or cars can make a significant difference. Trains, in fact:
- Pollute less.Nearly three-quarters of the EU’s total greenhouse gas emissions come from road transport, with more than half of those emissions produced by cars. Civil aviation is responsible for around 13%, while trains account for only 0.4%.
-
Are more cost-efficient for the climateThe environmental, climate, and health costs of trains (both high-speed and regular) are far lower than those of airplanes and cars. Only electric cars can have lower costs, but only when fully loaded with four passengers.

Why Consume Seasonal Food Products?
Seasonal food products (mainly fruits and vegetables, but also mushrooms and fish) are those that naturally reach their optimal consumption point during a specific time of the year. In contrast, out-of-season products are often imported and undergo preservation and processing techniques that can negatively impact their quality.
WHY CHOOSE SEASONAL PRODUCTS?
- They provide flavorful, nutrient-rich meals. Fresh, seasonal ingredients are packed with essential nutrients, vitamins, and antioxidants because they follow nature’s rhythms. Adjusting your diet according to the seasons leads to healthier eating, ensuring greater well-being for your body.
- They have a lower environmental impact. Seasonal cultivation requires less energy and water resources compared to non-seasonal crops and often needs fewer additives or chemicals.
- They are less expensive. Seasonal products are not only more nutritious but also more affordable. Their cultivation requires less energy, water, and fertilizers, which is reflected in their lower final cost.

Why Choose Organic Products?
Organic food products adhere to strict standards that exclude the use of synthetic chemicals in both farming and animal husbandry.
They are often a symbol of quality, authenticity, and a commitment to social and environmental responsibility. Choosing organic products is a significant step toward a healthier and more sustainable lifestyle.
*Reminder: Organic products are always marked with the EU “organic” logo
Other Reasons to Choose Organic:
- Less Exposure to Chemicals. Organic production avoids the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals that can be harmful to both human health and the environment.
- Limited Environmental Impact. Organic farming uses energy and natural resources responsibly. It helps preserve biological balances and biodiversity within ecosystems, while also improving soil fertility.
- Adherence to Ethical Standards. Organic animal products, such as meat, eggs, and dairy, focus on the health and well-being of the animals. These animals are raised in more “natural” conditions (with more space and access to the outdoors) and are not treated with hormones or antibiotics (except when necessary for the animal’s health).
- Support for Local Development. Organic practices tend to foster greater interaction among various economic and social stakeholders, creating positive impacts for the local community and economy.

Why choose Geographical Indications products?
Geographical Indications products boast unique characteristics linked to their geographical origin and traditional expertise. These products have received one of the following recognitions or certifications from the European Union.
Italy has the highest number: 326 agro-food products and 527 wines.
- High Quality: These products adhere to strict standards.
- Greater Assurance: They provide a higher level of traceability and food safety compared to other products.
- Support for Local Economy: These products support local production systems and economies due to their strong connection to the territory, production methods, and communities. They also contribute to preserving ecosystems and biodiversity.
Protected Designation of Origin (PDO)
PDO IS A QUALITY SCHEME THAT IDENTIFIES A PRODUCT:
- Originating from a specific place, region, or, in exceptional cases, a country;
- Whose quality or characteristics are due essentially or exclusively to a particular geographical environment and its intrinsic natural and human factors;
- Whose production phases occur within the designated geographical area.
For wine production, this scheme also implies that the grapes used are sourced exclusively from the designated geographical area and that the product is made from vine varieties belonging to the species Vitis vinifera. This includes Italian wines labeled with Controlled and Guaranteed Designation of Origin (DOCG) and Controlled Designation of Origin (DOC).
Protected Geographical Indication (PGI)
PGI IS A QUALITY SCHEME THAT IDENTIFIES A PRODUCT:
- For which at least one phase of production takes place in the designated geographical area;
- Originating from a specific place, region, or country;
- Whose given quality, reputation, or other characteristics are essentially attributable to its geographical origin./li>
For wine production, this scheme implies that at least 85% of the grapes used come exclusively from the designated geographical area, that production occurs within this area, and that the product is made from vine varieties belonging to the species Vitis vinifera or a cross between Vitis vinifera and other species of the genus Vitis. This includes Italian wines labeled with Indication of Geographical Typicality (IGT).
Traditional Specialty Guaranteed (TSG)
TSG IS A QUALITY SCHEME THAT IDENTIFIES A PRODUCT:
- Made using production, processing, or composition methods that correspond to traditional practices for that product or food
- or made from traditional raw materials or ingredients.

Why Support Local Small Producers?
Local small producers and artisans of taste have always played a key role in the social and economic fabric of Italy.
They are the ambassadors of the culture, traditions, and identity of their regions, with their products often distinguished by quality and attention to detail.
However, in the last ten years, we have witnessed a worrying decline in small producers and artisans of taste. The number of farms dropped by 30% between 2010 and 2020; considering that over 90% of these businesses are individual or family-run, the loss is substantial. The same downward trend can be observed in other sectors linked to the production and sale of local food and wine specialties.

Why hand down local recipes and culinary traditions?
Today, we live in an increasingly globalized world. While this phenomenon has allowed us to discover foods and recipes from nearby and distant countries, it is also leading us to forget or abandon our culinary traditions.
We are increasingly in the habit of eating out at least one meal and spending less time cooking-about an hour between breakfast, lunch, and dinner. The risk of losing what characterizes us is therefore high.
- They are the bridge between the past and the future. Recipes are not just a simple set of instructions for preparing a dish. They represent a connection to our roots, tell stories and anecdotes that link us to the past and guide us toward the future. They are a treasure to be preserved and shared with pride
- They represent a country in its diversity. Each territory has its own specialties, traditional techniques, and distinctive ingredients that are the result of history, geography, and local resources.
- They are part of our daily life. And they remind us of moments spent together around a laden table.

How to Navigate the World of Sustainability Certifications?
Sustainability certifications are seals or labels on various products that attest to compliance with specific environmental, social, and ethical standards. These can pertain to the origin of ingredients, farming practices, worker treatment, resource management, and more.
It’s advisable to trust certifications that are recognized at the European and international levels. These certifications are often identifiable by logos (some products may even include a traceability code) and are subject to periodic checks and controls by third-party organizations, separate from the issuing body.
WHAT ARE THE MAIN CERTIFICATIONS FOR PRODUCTS AND SERVICES?

How to Navigate the World of Sustainability Certifications?
FOR ALL TYPES OF DESTINATIONS, THERE ARE TWO SPECIFIC REFERENCES:
Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC):
The GSTC provides universal guidelines for sustainability in tourism, which serve as the foundation for various regional and national certifications. The GSTC sets and manages global standards for sustainable travel and tourism. These guidelines are divided into two categories:
1.Destination criteria, intended for public policymakers and destination managers.
2.Industry criteria, designed for hotels and tour operators.
These standards are the result of a global effort to develop a common language on sustainability in tourism and are organized into four pillars:
•(A) Sustainable management
•(B) Socioeconomic impacts
•(C) Cultural impacts
•(D) Environmental impacts
Since every tourist destination has its own unique culture, environment, customs, and laws, the criteria are designed to be adaptable to local conditions and supplemented with additional criteria specific to the location and activities.
European Tourism indicator system (ETIS):
ETIS is a self-assessment tool for evaluating sustainable management performance in terms of environmental, socio-cultural, and economic impact. Developed by the European Commission and implemented since 2013, this tool does not serve as a certification but helps improve sustainable management strategies by actively involving tourism businesses, residents, and other organizations within the sector.

How to calculate your ecological footprint?
The ecological footprint is an indicator used to assess human consumption of natural resources in relation to the Earth’s capacity to regenerate them. Measuring your own footprint is the first step in adopting a more sustainable lifestyle both at home and on vacation. But how to do it?
HERE IS A LIST OF ONLINE TOOLS THAT PROVIDE AN ESTIMATE BASED ON FACTORS SUCH AS DIET, ACCOMMODATION, AND TRANSPORTATION:
World Footprint Network: One of the most well-known global ecological footprint calculators. It offers a detailed analysis based on various factors such as energy consumption, diet, and lifestyle.
Carbon Footprint: This site focuses primarily on calculating the carbon footprint and also provides suggestions on how to reduce it.
WWF Footprint Calculator: Created by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), this tool is easy to use and focuses on daily consumption choices.
EPA’s Carbon Footprint Calculator: Provided by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, this tool is specifically designed for the American context but can also be used for a general overview.
+MyClimate: This Swiss tool is particularly detailed and also offers the option to offset your environmental impact through sustainability projects.
Resurgence Ecological Footprint Calculator: A tool that provides a more detailed analysis of individual activities and consumption choices.
Remember: Once you have calculated your footprint, you can take targeted actions to reduce it, including choosing seasonal and local foods, supporting producers who adopt sustainable practices, and selecting low-environmental-impact transportation options.